区间型
区间型
给定一个序列/字符串,进行一些操作
最后一步会将序列字符串去头/去尾
剩下的会是一个区间[i, j]
特点:
题目会存在Subarray/Substring相关的字眼
状态:
f[i][j]表示子串[i,j]时的性质,或f[i][k]表示以i开头长度为k的区间性质
用f[i][j]表示数组/字符串中[i,j]这一段区间的最优值/可行性/方案总数
题目特点:
题目会存在Subarray/Substring相关的字眼
大区间依赖小区间,循环方式不同
因此要从较小区间计算到较大的区间
转移:
大的 Subarray/Substring 的依懒于小的Subarray/Substringdp[i][j]=max/min/sum/or([i,j]之内更小的若干区间])
有的问题,需要第三重循环,枚举区间断点
子串问题,无需第三重循环,只需要判断两侧即可
解决方案:
- i 倒着循环,j 正着循环
- 先循环区间长度,加再循环区间起点
匹配类/端点
判断回文子串
状态:dp[i][j] 表示 i,j 这一段是不是回文串
转移:dp[i][j]=dp[i + 1][j - 1] and s[i] == s[j]
边界:dp[i][i]=true, dp[i][i + 1] == (s[i] == s[i + 1])
答案:dp[x][y]对于任意想要检测是否是回文串的下标范围 x-y
5. Longest Palindromic Substring
Given a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s.
LPS 最长回文子串(substring需要连续)
状态:f[i][j]表示 i,j 这一段是回文串
转移:f[i][j]=f[i+1][j-1]&&S[i]==[j]
边界:f[i][i]=true, f[i][i+1]=(s[i] == s[i + 1])
答案:更新时最长的段
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 2) {
return s;
}
int n = s.length();
int maxLen = 1, begin = 0;
// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i..j] 是否是回文串
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
// i 从字符串末尾开始向前遍历
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// j 从 i 开始向后遍历
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
// 2长度较短(<=3) 或者 内部子串也是回文
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
if (j - i < 3 || dp[i + 1][j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = true;
if (j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
}
}
return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen);
}516. Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence's length in s.
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
LPS 最长回文子序
状态:f[i][j]表示 i,j 这一段的最长回文子序列的长度
转移:f[i][j]=max{f[i+1][j], f[i][j-1], f[i+1][j-1]+2|S[i]==[j]}
边界:f[i][i]=1
答案:f[0][n-1]
按照区间长度j-i从小到大的顺序去算
加找最优解,加pi[i][j]数组,记录这个位置做的选择,0:干嘛,1:干嘛,3:干嘛
public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n][n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
dp[i][i] = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][n - 1];
}730. Count Different Palindromic Subsequences
Given a string s, return the number of different non-empty palindromic subsequences in s. Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
A subsequence of a string is obtained by deleting zero or more characters from the string.
A sequence is palindromic if it is equal to the sequence reversed.
Two sequences a1, a2, ... and b1, b2, ... are different if there is some i for which ai != bi.
int MOD = (int) 1e9 + 7;
public int countPalindromicSubsequences(String s) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
int n = cs.length;
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
int[] L = new int[4], R = new int[4];
Arrays.fill(L, -1);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
L[cs[i] - 'a'] = i;
Arrays.fill(R, -1);
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
R[cs[j] - 'a'] = j;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
if (L[k] == -1 || R[k] == -1)
continue;
int l = L[k], r = R[k];
if (l == r)
f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + 1) % MOD;
else if (l == r - 1)
f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + 2) % MOD;
else
f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + f[l + 1][r - 1] + 2) % MOD;
}
}
}
return f[0][n - 1];
}分割类/合并/断点
Matrix Chain Pattern
最典型的区间 DP,复杂度通常为 。
核心逻辑:我想解决区间 的问题,必须在中间切一刀(枚举 ),把它分成 和 两部分,然后合并。这本质上就是记忆化的分治。
On3 Floyd
1039. Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon
状态:f[i][j]表示剖分ij之间的节点的最小score
转移:f[i][j]=f[i][k]+f[k][j]+a[i]*a[k]*a[j]
public int minScoreTriangulation(int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
for (int i = n - 3; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 2; j < n; j++) {
f[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = i + 1; k < j; k++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i][k] + f[k][j] + values[i] * values[j] * values[k]);
}
}
}
return f[0][n - 1];
}1000. Minimum Cost to Merge Stones
There are n piles of stones arranged in a row. The ith pile has stones[i] stones.
A move consists of merging exactly k consecutive piles into one pile, and the cost of this move is equal to the total number of stones in these k piles.
Return the minimum cost to merge all piles of stones into one pile. If it is impossible, return -1.
一条直线上有 N 堆石头,每次可以合并连续的 K 堆石头,代价是 K 堆石头之和,问最终需要合并成一堆的最小代价之和
状态:f[i][j][k]表示i到j这一段合并为k堆石子的最小代价
转移:f[i][j][k]=min{f[i][x][k-1]+f[x][j][1]}+sum(i,j)
答案:f[0][n-1][1]
状态优化:
状态:f[i][j]表示i到j合并到不能合并的最小花费
转移:f[i][j]=min[m,i,j-1,k-1]{f[i][m]+f[m+1][j]}+sum(i,j)|(j-i)%(k-1)==0
答案:f[0][n-1]
四边形优化
public int mergeStones(int[] stones, int m) {
int n = stones.length;
if ((n - 1) % (m - 1) != 0) {
return -1;
}
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
int[] preSum = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
preSum[i + 1] = preSum[i] + stones[i];
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
f[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = i; k < j; k += m - 1) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i][k] + f[k + 1][j]);
}
if ((j - i) % (m - 1) == 0) {
f[i][j] += preSum[j + 1] - preSum[i];
}
}
}
return f[0][n - 1];
}312. Burst Balloons
需要在数组前后各加1
状态:dp[i][j]表示戳爆 i和j之间所有气球之后(含i,j)的最大积分
转移:dp[i][j] = max{dp[i][k-1] + dp[k+1][j] + nums[i-1] * nums[k] * nums[j+1]} i<=k<=j
边界:
答案:dp[0][n-1]
特殊定义:(不推荐,临场发挥容易失误)
状态:dp[i][j]表示戳爆 i和j之间所有气球之后(不含i,j)的最大积分
转移:dp[i][j] = max{dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] + nums[i] * nums[k] * nums[j]} i<k<j
答案:dp[0][n-1]
1547. Minimum Cost to Cut a Stick
Given a wooden stick of length n units. The stick is labelled from 0 to n. For example, a stick of length 6 is labelled as follows:
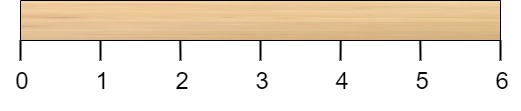
Given an integer array cuts where cuts[i] denotes a position you should perform a cut at.
You should perform the cuts in order, you can change the order of the cuts as you wish.
The cost of one cut is the length of the stick to be cut, the total cost is the sum of costs of all cuts. When you cut a stick, it will be split into two smaller sticks (i.e. the sum of their lengths is the length of the stick before the cut). Please refer to the first example for a better explanation.
Return the minimum total cost of the cuts.
状态:dp[i][j]表示戳爆 i和j之间所有气球之后(含i,j)的最大积分
转移:dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][k-1] + dp[k+1][j]} + nums[j+1] - nums[i-1]} i<k<j
边界:
public int minCost(int n, int[] cuts) {
int len = cuts.length;
Arrays.sort(cuts);
int[] vals = new int[len + 2];
vals[len + 1] = n;
System.arraycopy(cuts, 0, vals, 1, len);
int[][] f = new int[len + 2][len + 2];
for (int i = len; i > 0; i--) {
f[i][i] = vals[i + 1] - vals[i - 1];
for (int j = i + 1; j <= len; j++) {
f[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i][k - 1] + f[k + 1][j]);
}
f[i][j] += vals[j + 1] - vals[i - 1];
}
}
return f[1][len];
}矩阵乘法的最小花费
状态:f[i][j]表示i到j连乘的最小花费
转移:f[i][j]=min{f[i][k]+f[k+1][j]+pqr}
边界:f[i][i]=0
矩阵乘法的方案数
状态:f[i][j]表示i到j连乘的方案数
转移:f[i][j]=sum{f[i][k]*f[k+1][j]}
边界:f[i][i]=1
双区间
扰乱字符串 Scramble String
这里所有串都是S和T的子串,且长度一样
所以每个串都可以用(起始位置,长度)表示
状态:f[i][j][k]表示S1能否通过变换成为T1
- S1为S从字符i开始的长度为k的子串
- T1为T从字符j开始的长度为k的子串
转移:f[i][j][k]=or{f[i][j][w]&&f[i+w][j+w][k-w] or f[i][j+k-w][w]&&f[i+w][j][k-w]}
边界:f[i][j][1]=s[i]==s[j]
答案:f[0][0][n]
空间复杂度为record数组,长度为n; 每个子数组record[i]最多不超过i(组合数)*i(每个字符串长度)个字符; 求和(12+22+...+n^2=>O(n3)), 故空间复杂度的上限为O(n3)
